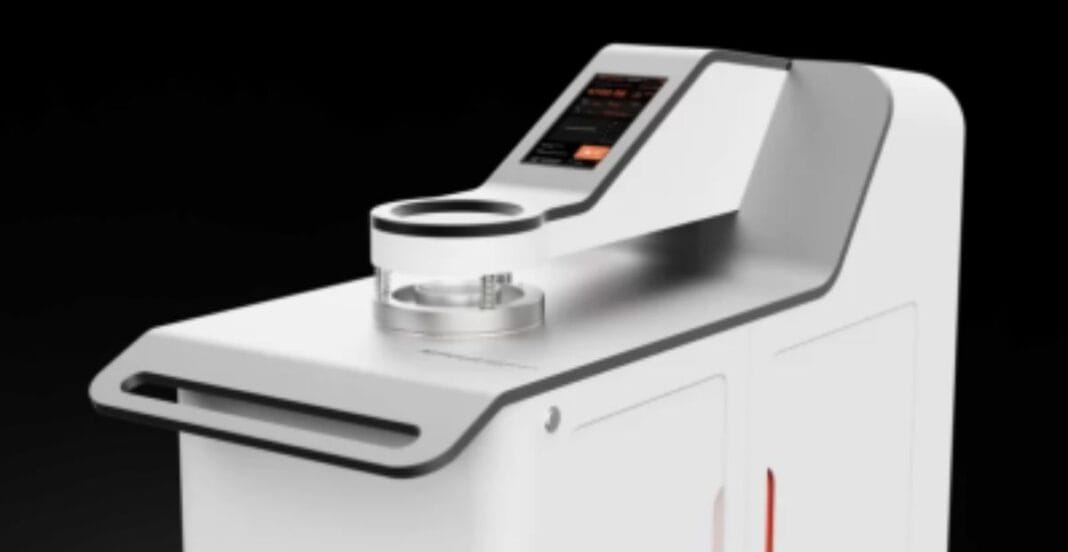
Introduction-
As a property air permeability is associated with comfort and functionality within hosiery fabrics and nonwoven materials. Moreover, performance features of modern apparel such as woven garments, automotive seat covers, construction fabrics and insulating clothes necessitates monitoring of this measurement. Garment textiles air permeability tester is the apparatus designed specifically for the analysis of permeable flow of air through fabrics and materials in controlled conditions. This article analyses the operating principles as well as the applicability, advantages, and to some extent standards of air permeability testing devices.
What is an Air Permeability Tester?
An Air Permeability Tester is an equipment in a lab used to determine the volume of air that passes through a known area of a fabric or any porous material placed perpendicular to the direction of airflow under a certain mechanical pressure. This results is usually given as a function of time. Usual units transformed into standard measurement like millimeters per second (mm/s) or cubic centimeters per square centimeter per second (cm³/cm²/s) or liters per square meter per second (l/m²/s) .
How Does an Air Permeability Tester Work?
An air permeability tester works on the principle of Darcy’s Law regarding flow of fluid in porous media. Each tester has an appropriate measurement head where a test specimen is well clamped. Then, a defined pressure difference is set over the specimen. In this case, the tester calculates the amount of air flowing through the material in the given period of time.
Key components of an air permeability tester typically include:
- Test Head and Clamp, which enable sample retention.
- Pressure Chamber that facilitates generation of pressure difference.
- Flow Meter or Mass Flow Sensor Sets that allow measurements of amount of air that flows.
- Display that could be analog or digital for showing results and their interpretation.
- Vacuum and Pressure Control units that facilitate controlled conditions.
Microprocessors control the majority of today’s gadgets, and they adjust automatically depending on the materials used and the standards set.
Standards Governing Air Permeability Testing
Testing the air permeability of a material is provided by a number of international sets of standards. The most known standards include:
- ASTM D737 – Standard Test Method for Air Permeability of Textile Fabrics
- This is the most widely used standard, measuring air permeability in cubic feet per minute per square foot (cfm/ft²) or cm³/s/cm².
- ISO 9237 – Textiles — Determination of the permeability of fabrics to air
- This standard specifies test conditions including test area, pressure drop, and measurement units (typically l/m²/s).
- BS 5636 – Method for Determination of Air Permeability of Fabrics
- EN ISO 9073-15 – For nonwoven materials
- TAPPI T251 – For paper and packaging applications
Each standard as listed above differ from one another and contain variances in terms of specimen test pressure, specimen size, and evaluation criteria. The right one has to be chosen according to the particular application and use of the material.
Applications of Air Permeability Tester
Apparel and Activewear
Breathability is prioritised when it comes to sportswear and outdoor clothing. Fabrics which have high air permeability maximize comfort by facilitating airflow and assisting in heat expulsion.
Medical Textiles
In the case of surgical gowns, masks, and wound dressings, controlled air permeability protects while providing the desired breathability.
Automotive Interiors
The seats of a car, headlining and carpets possess accurate air permeability for comfort, sound absorption, and durability of the material.
Industrial Filters
The performance of the filter greatly relies upon the air permeablility of the filter media. Thea testing conducted ensures compliance with performance and safety standards.
Technical and Protective Textiles
Air permeability testing is fundamental for evaluating textiles used in military uniforms, firefighter suits, and hazmat suits because these garments are required to be both breathable and protective.
Nonwovens
Hygiene products such as diapers and sanitary pads optimize air permeability to ensure comfort while maintaining fluid barrier properties.
Construction materials
Insulation and waterproofing provided by membranes in roofing and wall applications must be vapor permeable.
Types of Air Permeability Testers
Used in high-throughput labs, these systems capable of testing numerous samples concurrently in uniform conditions.
Manual Air Permeability Testers
Suitable for small-scale labs, these basic models with pressure set manually and airflow read on analog gauges.
Digital Air Permeability Testers
Researchers and quality assurance professionals use these devices, which feature digital pressure control, automatic data logging, and touchscreen interfaces.
Multi-Head Air Permeability Testers
Used in high-throughput labs, these systems capable of testing numerous samples concurrently in uniform conditions.
Portable Air Permeability Testers
Battery-operated and lightweight units intended for on-site or field-testing, especially in construction and large-scale textile manufacturing plants.
Key Performance Features to Consider
- Pressure Range and Control
The feature of adjustable pressure differentials enables the system to function with multiple material types. - Measurement Accuracy
Automatic calibration features combined with high-precision flow sensors provide accurate and consistent test results. - User Interface
User experience benefits from touchscreen control panels along with USB data export capabilities and multilingual interfaces. - Software Integration
Advanced systems provide connectivity to PCs and include data management software that enables tracking capabilities alongside analysis mechanisms and report production. - Compliance with Test Standards
Test the instrument to confirm conformity with major standards including ASTM D737 and ISO 9237. - Sample Holder Versatility
The system uses interchangeable test plates and adjustable clamping rings to test samples of different sizes and thicknesses. - Maintenance and Support
Select a system that features durable construction with components that are easy to clean along with robust technical support.
Interpreting Test Results
Factors like material type and end-use requirements along with existing standards should guide the interpretation of air permeability test results. For example:
Sportswear demands high air permeability values greater than 1000 l/m²/s but barrier fabrics must avoid such levels.
A low air permeability measurement of less than 10 l/m²/s points to tight weave structures which are perfect for creating windproof jackets and waterproof membranes.
Manufacturers utilize graphical data trends and deviation reports along with quality thresholds to ensure fabric specifications meet their product performance objectives.
Common Testing Challenges
1.Fabric distortion due to high pressure
2.Leakage from poor sample clamping
3.Environmental influences (humidity, temperature)
4.Repeatability across operators or devices
5.Calibration drift over time
To reduce measurement errors it is essential to implement routine calibration and standardization protocols.
Future Trends in Air Permeability Testing
- AI and Machine Learning Integration
Predictive algorithms will soon enable accurate predictions of fabric performance based on air permeability information to support smart textile development. - Sustainability Applications
The assessment of airflow properties in biodegradable and recycled materials helps in creating environmentally sustainable designs. - Smart Textile Adaptation
Wearable electronics can gain better breathability monitoring by integrating micro-sensors for real-time data collection. - Enhanced Automation
Efficiency in high-volume testing environments will improve through robotic sample handling combined with batch testing methods. - Cloud-Based Testing Platforms
Centralized software enables remote access to test results and provides automated report generation with inter-lab collaboration features.
Conclusion-
The air permeability of textiles stands as a crucial property that affects comfort levels, functional performance and safety standards within various industrial sectors. The Air Permeability Tester stands as a fundamental instrument for measuring air permeability under consistent and replicable conditions. The necessity for precise and quick air permeability testing will become more significant as market demands for advanced sustainable materials with multiple functions continue to rise.
Knowledge of Air Permeability Testers’ principles, applications and technical abilities enables manufacturers, researchers and quality assurance specialists to make decisions that enhance product performance and fulfill market requirements.
Companies developing breathable sportswear, protective gear and efficient filter media achieve reliability and market advantage through air permeability testing in their quality control procedures.


